As global trade enters the next chapter of digitization, a silent yet powerful legal instrument is reshaping the way we exchange, finance, and secure goods across borders: the UNCITRAL (United Nations Commission on International Trade Law) has created the Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records (MLETR). While not as publicly celebrated as blockchain or AI, this 2017 framework is the legal foundation enabling true paperless trade and it’s already transforming global supply chains.
Why MLETR Matters for Supply Chain Leaders
Every day, trillions of dollars’ worth of goods move across oceans, borders, and markets. Yet much of this commerce relies on paper-based documents like bills of lading, warehouse receipts, and promissory notes. These documents must be physically endorsed, transferred and stored.
This paper trail creates bottlenecks:
- Delays in customs and clearance
- High costs of courier services and document handling
- Fraud risks due to lack of verifiability
- Lack of traceability in multi-party ecosystems
The MLETR addresses these pain points by giving legal equivalence to electronic versions of these transferable documents. In short: what used to require a pen and paper can now be done with code and cryptography in case it is approved legally by the authorities.
🛠️ What MLETR Enables in Supply Chains
- Electronic Bills of Lading (eBL)
Carriers, forwarders, and shippers can now issue and transfer bills of lading digitally, reducing issuance time from days to seconds. - Digital Trade Finance
Banks can accept and process electronic trade documents, enabling real-time financing and automated compliance checks. Imagine that you issue a 100% digital credit note. - Blockchain-Integrated Supply Chains
MLETR complements smart contracts and tokenized assets, allowing automated ownership transfer of goods tied to IoT events. - ESG and Compliance Alignment
Digitization contributes to paperless sustainability goals and audit transparency, particularly for ESG reporting.
✅ Countries Leading the Change
Until now, 10 jurisdictions have officially adopted laws based on the MLETR. Some of them as as follows:
- Bahrain (2018 – first mover)
- Singapore, UK, France, Paraguay
- Belize, Kiribati, Papua New Guinea, Timor-Leste
- Abu Dhabi Global Market (free zone in UAE)
These trailblazers are not necessarily trade giants, but their forward-thinking stance creates competitive advantage. For example, Singapore’s Electronic Transactions (Amendment) Act 2021 enabled the port ecosystem and banks to digitize end-to-end marine trade processes.
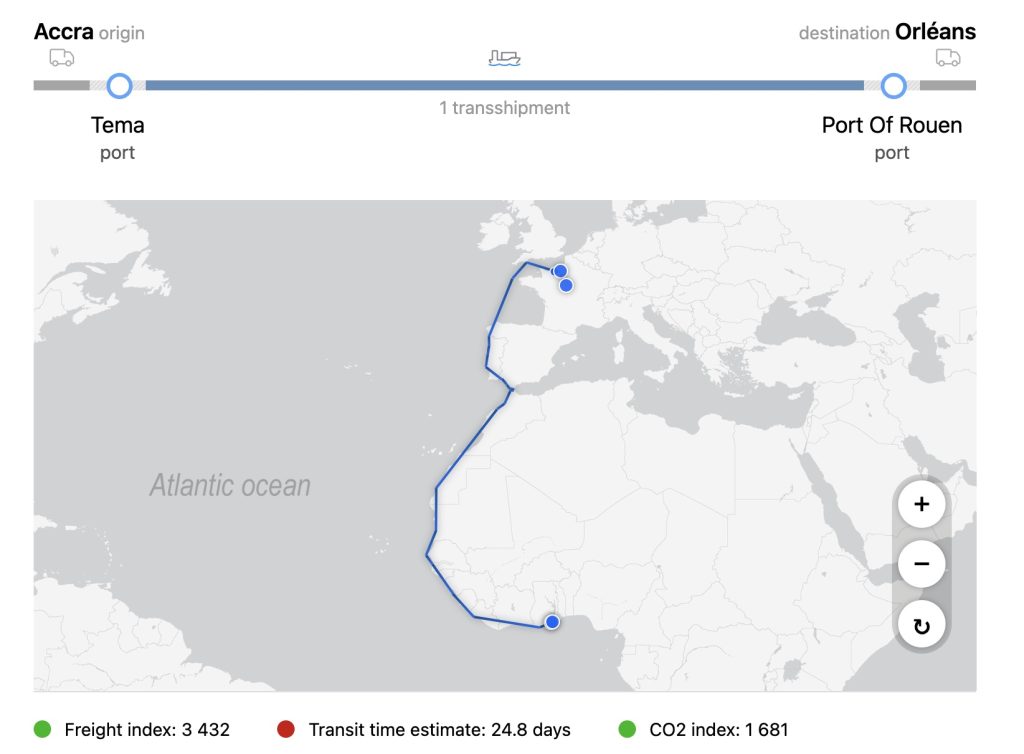
🚢 Real-World Impact: A Scenario
Imagine you’re exporting cocoa beans from Ghana to a confectionery factory in France. With MLETR-based digital documents:
- The exporter issues an e-bill of lading through a secure platform.
- The buyer receives it in seconds and initiates payment using a smart contract.
- A bank in Paris finances the trade immediately by verifying authenticity.
- Customs clearance is automated, thanks to shared digital records.
- The shipment arrives days earlier, with lower financing and logistics costs.
What used to be a 3-week documentation process which is paper-heavy ordeal becomes a seamless 3-day transaction in total (excluding the transit time).
📊 Strategic Takeaways for Supply Chain Leaders
- Advocate for Legal Reform
If your country hasn’t adopted MLETR, engage industry associations and regulators to push for it. The competitive edge is real. - Digitize Internal Workflows
MLETR is only as useful as your ability to generate and process e-documents. Invest in compatible platforms and ERP integrations. - Partner with Digital Trade Platforms
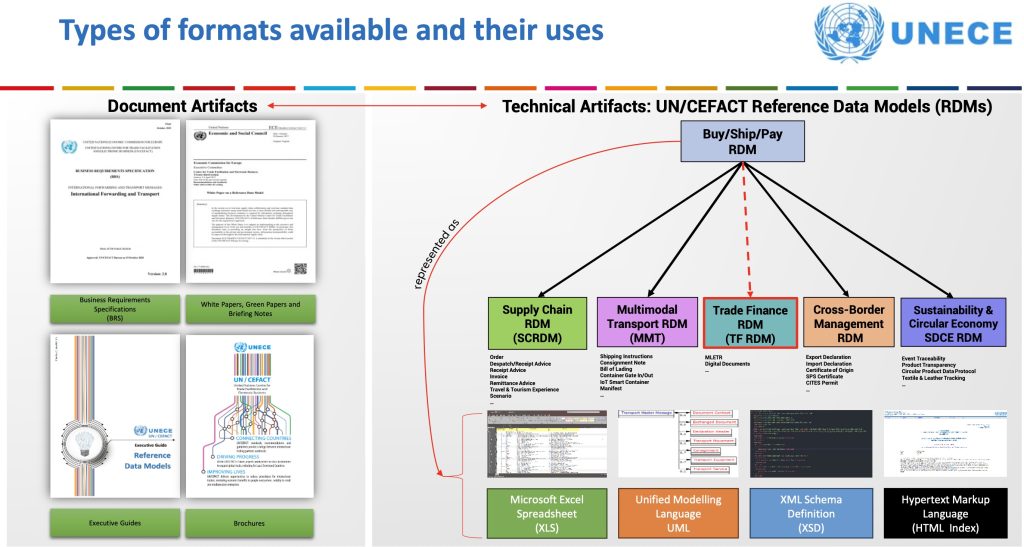
Solutions like WaveBL, TradeLens, and Contour are already MLETR-compliant. Early adoption positions your company for trade fluidity. If you want to know about the data standards. Have a look at UN/CEFACT details. - Educate Your Teams
Legal, procurement, logistics, and finance teams need to understand what MLETR is and how it changes their daily operations.
🔮 The Road Ahead
In the next 3–5 years, MLETR adoption will likely explode, especially as the G7 countries move toward harmonized digital trade frameworks. This shift will redefine trade logistics, reshape the role of intermediaries, and elevate digital trust as a currency of commerce.
The organizations that prepare today will gain tomorrow. Those that delay may find themselves competing in a game where others have already digitized the rules.
Final Thought
As a global supply chain professional, I see MLETR not just as a legal tool, but as a strategic enabler. It’s time we moved beyond digital pilots and truly embraced the legal backbone of 21st-century trade.
Let paper be a relic and replace it with electronic documents for global trade.
