Introduction
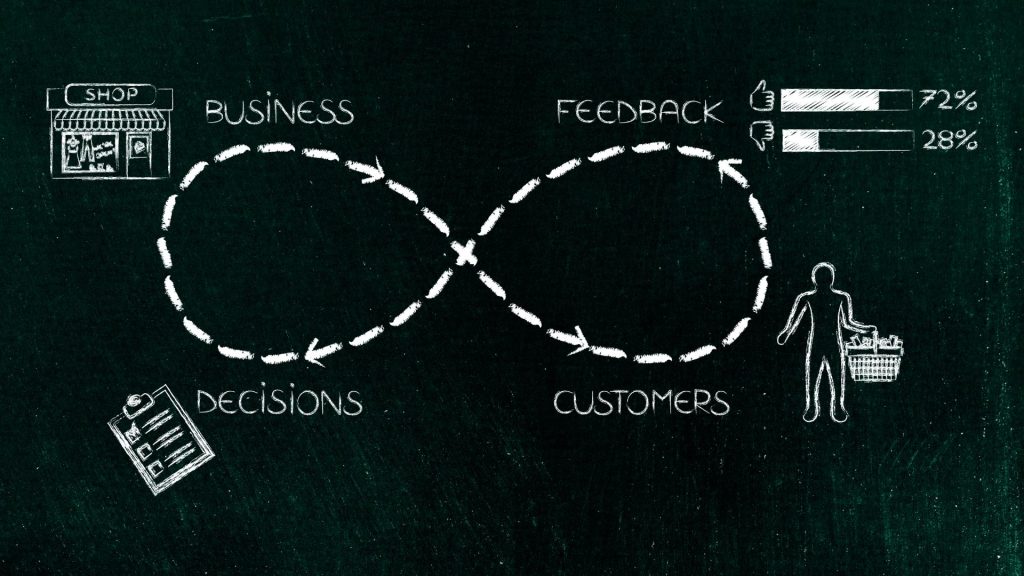
Information-feedback control systems are the backbone of all life and human activity, from biological evolution to advanced technological systems. As Jay W. Forrester, the pioneer of system dynamics, once said:
“Everything we do as individuals, as an industry, or as a society is done in the context of an information-feedback system.”

This principle is especially critical in supply chain management (SCM), where information flow and feedback loops determine efficiency, resilience, and adaptability. In this blog, we explore how information-feedback systems shape modern supply chains and why they are essential for success.
What Are Information-Feedback Control Systems?
An information-feedback control system is a closed-loop mechanism where outputs are continuously monitored and fed back into the system to adjust inputs, ensuring optimal performance. These systems are present in:
- Nature as homeostasis in living organisms
- Technology as automated inventory control, IoT devices for better service
- Business as demand forecasting and replenishment
In supply chains, feedback loops help organizations respond dynamically to changes in demand, supply disruptions, and market fluctuations.
How Information-Feedback Systems Power Supply Chains
Supply chains are complex networks involving suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and customers. Efficient SCM relies on real-time data and feedback to:
1. Demand Forecasting & Inventory Control
- Feedback Mechanism: Sales data → Demand forecasting algorithms → Inventory & Production adjustments for improved fullfilment
- Benefit: Prevents stockouts and overstocking, reducing costs.
2. Supplier Performance Monitoring
- Feedback Mechanism: Quality & delivery metrics → Supplier scorecards → Procurement strategy updates
- Benefit: Ensures reliable suppliers and minimizes disruptions.
3. Logistics & Transportation Optimization
- Feedback Mechanism: GPS & traffic data → Route adjustments → Faster deliveries
- Benefit: Lowers fuel costs and improves delivery times.
4. Customer Feedback Integration
- Feedback Mechanism: Customer reviews → Product/service improvements → Enhanced satisfaction and customer retention
- Benefit: Strengthens brand loyalty and market competitiveness.
Real-World Applications in Supply Chain Management
Amazon’s Dynamic Fulfillment System

Amazon’s supply chain is a benchmark for efficiency, largely due to its Dynamic Fulfillment System, which leverages AI-driven feedback loops to optimize operations in real time. Below, we delve deeper into how Amazon uses these feedback mechanisms to:
Optimize warehouse robotics for faster order processing.Reroute shipments dynamically to avoid delays.
1. Adjusting Inventory Based on Real-Time Demand Signals
Amazon’s AI systems analyze real-time sales data, browsing behavior, and external factors (e.g., weather, trends) to dynamically adjust inventory levels across its global fulfillment network.
- Predictive Demand Forecasting: AI models process historical sales, seasonal trends, and even social media signals to predict demand spikes (e.g., Cyber Monday saw forecasts for 400M+ daily orders).
- Multi-Echelon Inventory Optimization: Inventory is strategically distributed across warehouses based on regional demand, reducing stockouts and overstocking. For example, the Sequoia system stores 30M+ items closer to customers, cutting fulfillment times by 25%.
- Automated Replenishment: AI triggers restocking orders when thresholds are breached, ensuring high-demand products are always available.
2. Optimizing Warehouse Robotics for Faster Order Processing
Amazon’s fulfillment centers rely on AI-powered robotics to streamline operations, with feedback loops ensuring continuous improvement.
- Sequoia System: A robotic inventory management system that identifies and retrieves items 75% faster than manual processes.
- Proteus Autonomous Robots: Navigate warehouses autonomously, transporting packages while avoiding obstacles, improving safety and speed.
- Sparrow Robotic Arm: Uses computer vision and AI to handle 200M+ unique products, reducing mis-picks and delays.
Feedback Loops in Action:
- Real-time performance data from robots (e.g., picking accuracy, movement efficiency) is fed back into AI models to optimize workflows.
- During peak seasons, robotic systems scale to handle 110K+ packages/day (up from 60K).
3. Dynamically Rerouting Shipments to Avoid Delays
Amazon’s logistics network uses AI to monitor and adapt to disruptions in real time.Key Systems:
- AI-Powered Route Optimization: Adjusts delivery paths based on traffic, weather, and carrier capacity. For example, during COVID-19, AI rerouted shipments to avoid bottlenecks.
- Load Balancing Algorithms: Distributes shipments across delivery stations to prevent congestion.
- Project P.I. (Private Investigator): Uses generative AI + computer vision to inspect packages for damage before shipping, reducing returns by 20%.
Feedback Loops in Action:
- Delivery performance data (e.g., delays, carrier reliability) is continuously analyzed to refine routing decisions.
- AI predicts delays before they occur, allowing preemptive rerouting.
Toyota’s Just-in-Time (JIT) System

Toyota’s JIT operates as a pull system, meaning production is triggered by actual demand rather than forecasts. This lean manufacturing approach relies on real-time signals between assembly lines and suppliers to maintain optimal inventory levels.
1. Kanban: The Visual Feedback System
- Kanban cards (or digital alerts) signal when parts are needed.
- When a part is used on the assembly line, a Kanban is sent to the supplier for replenishment.
- This ensures zero excess inventory while preventing shortages.
Example: If a Toyota factory uses 100 brake pads per hour, Kanban signals ensure suppliers deliver exactly 100 pads to the supplier; no more, no less.
2. Takt Time: Aligning Production with Demand
This metric ensures assembly lines match the exact pace of customer orders, avoiding overproduction.
Takt Time = (Available Production Time) / (Customer Demand)
Challenges & Solutions in Implementing Feedback Systems
While feedback-driven supply chains offer immense benefits, challenges include:
- Data Silos: Lack of integration between systems.
- Solution: Implement interfaces and IoT for seamless data sharing.
- Delay in Feedback: Slow response times lead to inefficiencies.
- Solution: Use AI and predictive analytics for real-time adjustments.
The Future of Feedback-Enabled Supply Chains
As supply chains grow more complex, the role of information-feedback control systems becomes even more critical. Companies that leverage real-time data, AI, and closed-loop feedback mechanisms will lead in:
✔ Agility – Faster response to disruptions.
✔ Efficiency – Reduced waste and lower costs.
✔ Customer Satisfaction – Better alignment with market needs.
By embracing Forrester’s principles of system dynamics, businesses can build smarter, self-correcting supply chains that thrive in an ever-changing world.
Is your supply chain leveraging feedback control systems effectively?

2 thoughts on “The Role of Information-Feedback Control Systems in Supply Chain Management”